Home > SMT Assembly News
This article provides recommendations for choosing materials to manufacture multilayer PCBs that achieve two critical requirements: limit manufacturing problems (e.g., bowing or twisting, as well as mis-registering; and meeting performance standards. A successful PCB production begins with proper material selection. For a low number of board layers, your PCB manufacturers default materials are usually your best choice as they are reliable and cost effective. However, when designs have special requirements or incorporate a high number of layers, then it is worth a designer’s effort to become more familiar with the available material options, in order to make the best decisions for their product.
The most important material for PCB manufacturing is raw laminate. It also represents the largest cost of all other materials needed to produce a multilayer PCB. Raw laminate has a critical impact for the prices and the delivery time of PCBs. Due to the amount of material needed for PCB fabrication, it is essential to optimize the size of your designs; even a small difference in size can result in a significant difference in cost. Different materials incur different costs and possess different characteristics, but higher quality laminates are typically also more expensive. The following are some of the main characteristics to take note of when comparing properties of different laminates:
Tg = Glass Transition Temperature – Temperature at which a critical change of physical properties will occur. In the case of laminates, it transitions from a hard, glassy material into a soft, rubbery material
Td = Decomposition Temperature - Temperature at which the laminate chemically decomposes
Dk = Dielectric Constant (also referred to as ?r in electromagnetics) – Indicates the relative permittivity of an insulator material, which refers to its ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. For insulating purposes, a material with lower dielectric constant is better and in RF applications a higher dielectric constant may be desirable
Df = Dissipation Factor – Indicates the efficiency of an insulating material by showing the rate of energy loss for a certain mode of oscillation, such as mechanical, electrical, or electromechanical oscillation
Our fabrication facilities are located in China, so it is advisable to choose high-quality local laminates in order to minimize shipping cost and lead time. The flason S1000-H (Tg 150) laminate is generally our default choice for a high-performance, mid-Tg laminate. Shengyi S1000-H is comparable to Isola FR406 (Tg 150), a standard North American laminate option. As outlined in Table 2 below, FR406 does slightly outmatch flason S1000H in terms of Dielectric Constant and Dissipation Factor, but some clients may be willing to compromise on these factors for a lower cost and/or a faster lead time.
Table 1: Comparison of PCB Materials
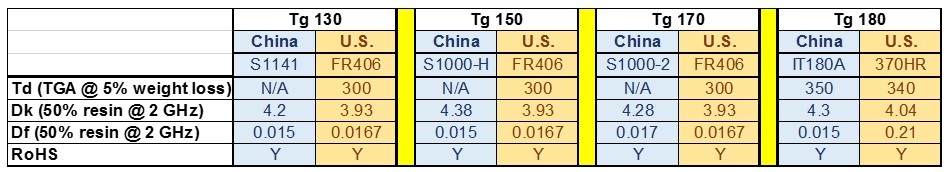
Flason S1141 (TG 130) is a good alternative to lower the cost of your project, at the sacrifice of some quality. In cases where higher quality is needed, we recommend Shengyi S1000-2M (TG 170) which is the closest in quality to Isola FR406 (Tg 170). Where quality is the highest priority, we would recommend utilizing ITEQ IT180A (TG 180) which is also RoHS compliant. ITEQ IT180A (TG 180) is comparable in quality and to Isola 370HR (TG 180). We at flason would suggest using flason S1000H (Tg 130) for typical projects. We would recommend using one of the higher quality laminate materials if any of these three conditions occur: if the PCB Design has 8 or more layers, if Copper Board is heavy with a copper weight heavier than 3oz, or if PCB Board is thin with a board thickness of less than 0.5mm.
The next element to consider is the dielectric thickness, which must be specified for impedance requirements. Multilayer materials range from 0.125mm to 1mm in thickness. Thin laminates (i.e. 0.1mm or less) are necessary for some low-power applications as well as the continued densification of multilayer circuit PCBs.
Table 2 lists the core material thickness with copper weight for normal FR4 Material
| Thickness including copper (mm.) | Copper Weight (oz.) |
| 0.145 mm. | H/H oz. |
| 0.17 mm. | 1/1 oz. |
| 0.185 mm. | H/H oz. |
| 0.2 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.25 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.3 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.4 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.5 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.6 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.7 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.8 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 0.9 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 1.0 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 1.1 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 1.2 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 1.5 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 1.6 mm. | 1/1 oz. or H/H oz. |
| 2.2 mm. | 1/1 oz. |
| 2.4 mm. | 1/1 oz. |
| 2.5 mm. | 1/1 oz. |
| 3.0 mm. | 1/1 oz. |
| Prepreg /Glass Styles | Pressed Thickness (mm) | Prepreg Resin content |
| 106 | 0.05 mm. | Approx. 73% |
| 1080 | 0.075 mm. | Approx. 65% |
| 3313 | 0.09 mm. | Approx. 57% |
| 2116 | 0.115 mm. | Approx. 55% |
| 7628 | 0.185 mm. | Approx. 46% |
| 7628H | 0.195 mm. | Approx. 51% |
Flason Electronics is capable of fabricating multi- layer PCB boards with a maximum copper weight of 10 oz. Copper weight of 4 oz. or higher will require an additional estimate, and may also affect lead times.
Keywords:
SMT Reflow Oven, Lead free Reflow Oven, Reflow Oven Manufacturer, LED reflow oven, PCB Reflow Oven, Nitrogen Reflow Oven, Dual Rail Reflow Oven, China Reflow Oven, wave soldering machine, Dual Rail Wave Soldering Machine, Nitrogen Wave Soldering Machine, Wave Soldering Machine Manufacturer.




Contact: Mr Tommy
Phone: +86 13691605420
Tel: +86 -755-85225569
Email: tommy@flason-smt.com
Add: 94#,Guangtian Road,Songgang Street,Bao an District Shenzhen China